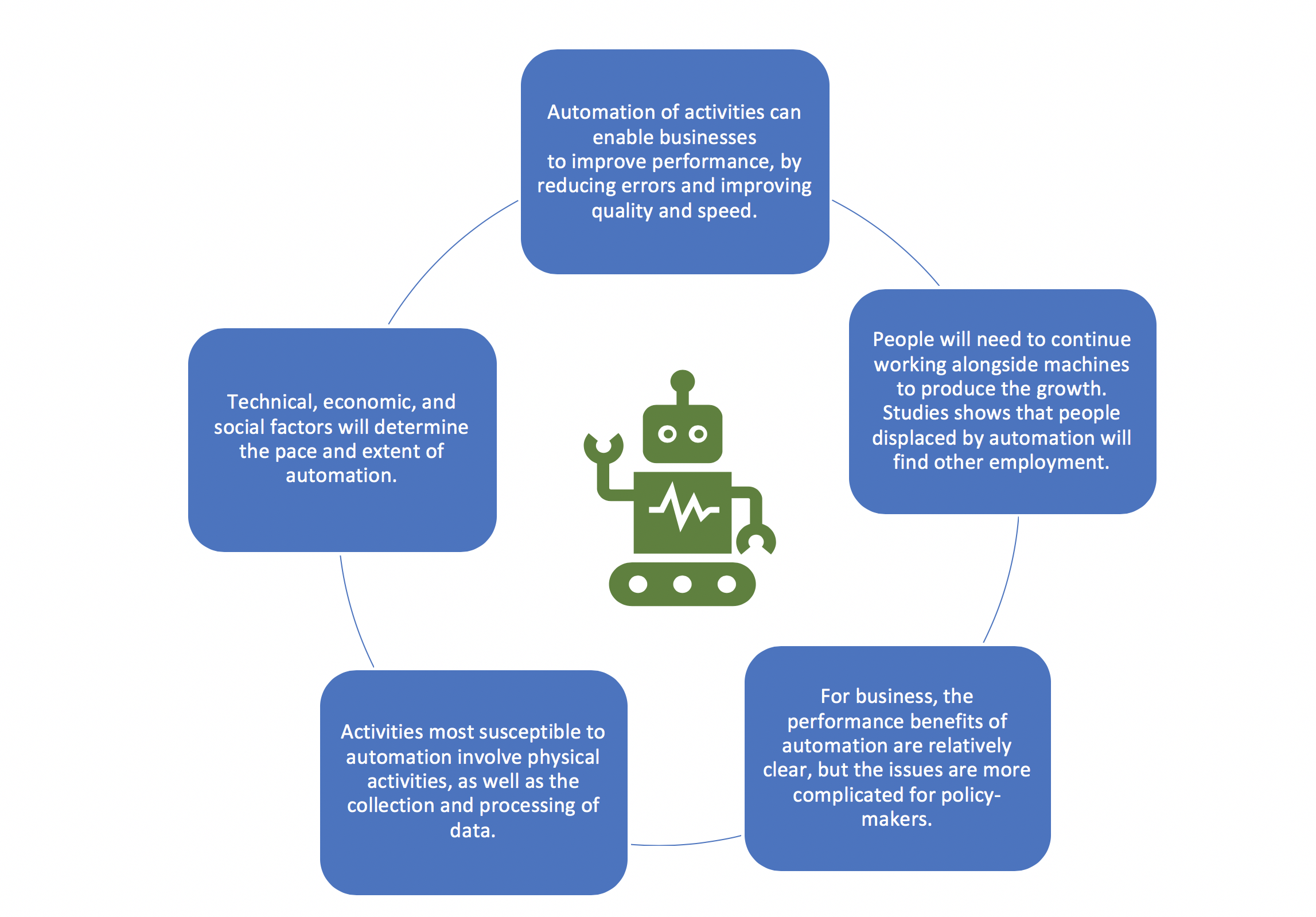
The impact of AI on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident, as research highlights the evolving dynamics of employment in response to technological advancements. Economists have noted significant trends reshaping job market trajectories, specifically within the framework of the future of work. As artificial intelligence transforms work environments, it is crucial to understand how technology and employment will adapt to these changes, including key AI workforce changes. By exploring job market trends driven by automated processes and innovation, we can better gauge the implications these shifts hold for various industries. Ultimately, the influence of automation in the workforce could redefine roles, necessitating new skills and strategies among workers to thrive in this changing landscape.
The effects of artificial intelligence on employment are significant and multifaceted, indicating a pressing need for adaptation among workers and employers alike. As society navigates the complexities of technological progress, discussions surrounding the evolution of work become essential. This includes examining how modern innovations are reshaping job responsibilities and market demands, ultimately leading to a redefined employment landscape. Emerging concepts such as workforce automation and shifts in labor patterns are critical to understanding these changes. As we chart the course of the upcoming job market, awareness of these evolving trends can help prepare individuals for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Understanding the Shift in the Labor Market Due to Technology
The labor market has always been in flux, deeply influenced by various technological advancements over the years. One significant insight from the recent study co-authored by economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers is the concept of occupational churn. This term captures the dynamic nature of job shares within different professions as technology reshapes what skills and roles are in demand. The analysis of over a century’s data reveals that although there was stability between the 1990s and 2017, recent findings suggest a notable uptick in job market volatility post-2019, linked to the rise of artificial intelligence and other generative technologies.
This transformation underscores a pivotal moment wherein traditional views on job displacement have been challenged. For instance, while earlier technological advancements caused fears regarding widespread unemployment, current trends indicate a more nuanced picture. As companies invest in AI and automation, certain job sectors may diminish, but new opportunities arise simultaneously, particularly in high-skill domains such as technology and engineering. Understanding these shifts is crucial for preparing the workforce for an increasingly automated future.
AI Impact on Labor Market: Emerging Trends
Artificial Intelligence is not merely another technological advancement; it marks a significant turning point in the job market, echoing previous shifts ignited by inventions such as the keyboard or electricity. The Harvard economists’ study identifies critical trends reflecting how AI shapes employment landscapes. One primary observation is the end of job polarization, which previously indicated an increase in low- and high-wage jobs, leaving a void in middle-income positions. Current patterns show a growing demand for highly skilled individuals, particularly in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), hinting at a future where skilled labor is increasingly prized.
As companies enhance their focus on AI, they are also funneling investments into technologies that promise greater productivity. This trend is leading to unprecedented growth in STEM jobs, which burgeoned from 6.5% to nearly 10% of the job market within just a decade. This stark uptick not only points to a recalibrated emphasis on technical proficiency but also suggests that the job market is adapting to favor individuals equipped with the skills to thrive in an AI-driven world. However, with these advancements comes the reality that some positions, particularly those in low-paid service roles, might not return as companies pivot towards automation.
Job Market Trends: The Rise of High-Skill Employment
In light of the rapidly changing landscape of work, recent studies indicate a clear transition toward high-skill employment opportunities. As economies evolve with advancing technologies, the labor market exhibits signs of favoring skilled roles, reinforcing the notion that adaptability and continuous learning will be paramount. For instance, the report highlights the increase in STEM positions, with jobs in this category seeing significant growth, which offers a glimmer of hope for those willing to invest in their education and training.
Moreover, the historical data analyzed by the economists illustrates how shifts in technology adoption can redefine career paths. The report conveys that higher wages and increased job opportunities for well-educated individuals contribute to a positive movement toward a knowledge-based economy. As businesses evolve, they will increasingly seek to employ a workforce that can leverage advanced technologies, reinforcing the importance of aligning educational programs with these emerging job market demands.
Automation in the Workforce: Navigating Challenges
The rise of automation in the workforce represents both opportunities and challenges for current and future job seekers. As automation technology continues to advance, industries such as retail have experienced significant job losses—evident in the considerable decline in retail sales positions due to the accelerated adoption of AI in e-commerce. This trend not only highlights the precarious nature of job security in these sectors but also reflects an essential shift towards online services that seamlessly integrate AI solutions.
Yet, while concerns about job displacement are valid, there remains a pressing need for workforce adaptability. Industries must prepare to retrain employees and re-skill workers whose jobs are most at risk, ensuring they can transition into emerging roles fueled by technological advancements. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and reskilling, workers can navigate the increasingly automated landscape without falling prey to obsolescence.
The Role of Continued Education in Adapting to Technological Change
Amid the seismic shifts brought about by technology and automation, the relevance of continued education has reached new heights. Workers must engage in lifelong learning to remain competitive in an evolving job market where new skills are constantly in demand. The Harvard economists’ research suggests that high-skilled jobs are on the rise, highlighting the essential role that education and training play in preparing individuals for these opportunities. Institutions must thus evolve curriculums to meet these emerging needs, emphasizing adaptability and technical proficiency.
Moreover, as AI and automation reshape the landscape, educational programs must also emphasize critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach will empower workers to thrive in a competitive environment where technology demands human adaptability and ingenuity. By fostering an educational ecosystem that prioritizes relevant skills, society can better navigate the challenges posed by technological disruptions in the labor market.
Future of Work: Embracing Change and Innovation
As we look towards the future of work, the ability to embrace change and innovation becomes critical for organizations and employees alike. The dynamic landscape shaped by AI, automation, and other technologies necessitates a proactive approach to workforce development. Companies that perceive change as an opportunity rather than a threat will likely lead the industry by cultivating an agile workforce adept at navigating technological uncertainty.
Furthermore, as workers adapt to new methods of operation and collaboration, the embrace of flexible remote work grows paramount. Acknowledging this shift enables organizations to harness talent from diverse geographical locations, promoting inclusivity and broadened access to job opportunities. The future of work is not merely about survival amidst disruption but leveraging technological advancements to build a more efficient and responsive workforce.
Technology and Employment: A Collaborating Future
The relationship between technology and employment is evolving into one based on collaboration rather than competition. Rather than viewing AI and automation as obstacles that threaten job security, workers can find ways to coexist and collaborate with these technologies to improve productivity. For instance, industries that have embraced AI have often reported enhanced efficiency, paving the way for more innovative workflow solutions and increased job satisfaction among employees who can focus on more complex tasks.
Additionally, as technology automates routine tasks, it allows professionals to redirect their time and energy toward strategic thinking, creativity, and problem-solving—qualities that remain rooted in human capabilities. The implication for the workforce is clear: Resilience and collaboration between workers and machines will be essential for maximizing the benefits of technological advancements in the labor market.
The Future of Labor: Preparing for Uncertainty
As the labor market continues to evolve under the influence of advanced technologies, it is crucial to prepare for uncertainty. Potential disruptions may arise from various sectors due to automation and AI, encouraging both workers and organizations to adopt a mindset geared toward innovation and resilience. By anticipating the ramifications of technology on employment, policy-makers and business leaders can develop strategies that mitigate risks and promote growth in emerging industries.
Employers can also take proactive measures by offering training programs that equip employees with abilities relevant for the future of work. This holistic approach acknowledges the inevitability of change and emphasizes preparedness and adaptability as vital components for navigating a turbulent job market. Ultimately, fostering a culture of innovation will be instrumental in shaping a workforce that not only survives but thrives in an AI-enhanced landscape.
Addressing the Skills Gap: Bridging Education and Employment
A significant impact of technological advancements in the labor market is the emerging skills gap that threatens workforce readiness. As companies adopt AI and automation, the demand for skilled workers grows, leaving a crucial gap for those who lack relevant training. Bridging this gap is essential for connecting educational programs with industry needs, ensuring that the next generation of workers can effectively enter the job market equipped with the necessary skills.
Educational institutions play a pivotal role in this endeavor by adapting curricula and offering certifications that align with current job market demands. Introducing vocational training programs, community partnerships, and mentoring opportunities can also facilitate real-world experience, allowing students to seamlessly transition from education to employment. Addressing the skills gap will be crucial in maintaining a resilient labor market capable of embracing the future of work.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting the future of work and the labor market?
AI is significantly influencing the future of work by reshaping job roles and employment patterns. Research indicates a shift towards high-paying, skilled jobs while traditional low-paying positions decline. For example, jobs in STEM fields have surged, indicating that the labor market is evolving alongside AI advancements.
What are the trends in job market changes due to AI workforce changes?
Recent studies highlight four key trends in job market changes due to AI: a shift towards high-skill jobs, an increase in STEM employment, a decline in low-paid service jobs, and a significant reduction in retail jobs. This reflects a broader transformation in the labor market, where AI-driven automation is reshaping the landscape.
Is automation in the workforce leading to job displacement, and how is this affecting the labor market?
Yes, automation in the workforce, particularly through AI technologies, has contributed to job displacement in various sectors, particularly in retail and low-paid service roles. While some job categories are increasing, many traditional roles are declining, leading to a more polarized job market where high-skill positions are favored.
What role does technology and employment play in the transformation of the labor market?
Technology and employment are closely linked as advancements, especially AI, redefine job descriptions and requirements. The long-term impact of these technologies suggests a continued demand for high-skilled workers, creating challenges for those in vulnerable job categories. This dynamic necessitates ongoing workforce adaptation to remain competitive.
Can we predict job market trends related to AI’s influence on the labor market?
Yes, job market trends indicate increasing demand for technology-oriented positions while traditional low-skill jobs face decline. Monitoring these trends helps predict future employment landscapes, suggesting that adaptation to new technology and upskilling will be essential for workers moving forward.
What evidence supports the idea that AI is a breakthrough technology affecting the labor market?
Research indicates that AI has become a breakthrough technology likened to historical advances like electricity and computing. The economic impact of AI is evidenced by rising investments in AI capabilities, increased hiring in STEM fields, and significant shifts in employment patterns, hinting at a transformative effect on the labor market.
How does AI affect job polarization in the current labor market?
AI is contributing to a nuanced form of job polarization, where growth is evident at the high end of the wage distribution. Recent data shows an upward trend in high-paying, skilled jobs, reducing the growth of middle-paying roles and increasing the prevalence of low-paid jobs, thus reshaping the wage landscape.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Polarization Transition | The labor market shows a shift toward growth in high-paid jobs with extensive training, moving away from the previous polarization of low-paid and middle-income jobs. |
| Increase in STEM Jobs | There has been a nearly 50% increase in STEM jobs from 2010 to 2024, emphasizing the rising demand for tech talent in the job market. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Service Jobs | Flat or decreasing employment in low-paid service roles since 2019 suggests a potential reduction in these job opportunities due to various economic factors. |
| Significant Drop in Retail Sales Jobs | A 25% reduction in retail sales jobs between 2013 and 2023, attributed to the impact of e-commerce and predictive AI technologies. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is significant and increasingly evident as economists analyze over a century of technological disruption. The recent trends indicate a transformation in job dynamics, highlighting the shift towards high-skilled positions while also revealing a worrying decline in traditional low-paid service jobs. As AI continues to reshape our workforce, it’s imperative for workers across all sectors to adapt to these changes or risk displacement.